The Evolution of Virtual Reality in Gaming: From Concept to Mainstream Sensation
From Concept to Mainstream Sensation
Introduction:
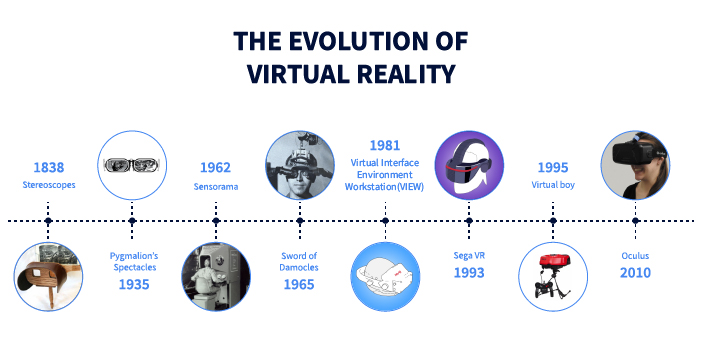
The journey of virtual reality (VR) in gaming is a tale of innovation, perseverance, and technological breakthroughs that have reshaped the gaming landscape. From its humble beginnings as experimental prototypes to its current status as a mainstream sensation, VR gaming has undergone a remarkable evolution that has captivated players and developers alike.
Pioneering Beginnings: Early Experiments and Prototypes:
The roots of VR gaming can be traced back to the 1960s and 1970s, when researchers and engineers began exploring the possibilities of immersive technology. Early experiments, such as Ivan Sutherland’s “Sword of Damocles” and the Sensorama machine developed by Morton Heilig, laid the groundwork for what would eventually become modern VR gaming. These pioneering efforts introduced concepts such as head-mounted displays, motion tracking, and immersive environments, setting the stage for future advancements in the field.
Pioneering Beginnings: Early Experiments and Prototypes in Gaming:
The origins of modern gaming can be traced back to the early experiments and prototypes that laid the foundation for the industry we know today. In these formative years, visionary thinkers and innovative engineers embarked on a journey to explore the possibilities of interactive entertainment, paving the way for the evolution of gaming into the multi-billion dollar industry it is today. This article delves into the pioneering beginnings of gaming, highlighting the early experiments and prototypes that set the stage for the digital revolution that would follow.
The Birth of Interactive Entertainment:
The concept of interactive entertainment dates back to the mid-20th century when researchers and engineers began to explore the potential of electronic devices to create immersive experiences. One of the earliest examples of interactive entertainment was the creation of electronic games such as “Spacewar!” in 1962, developed by MIT students Steve Russell, Wayne Wiitanen, and others. “Spacewar!” was a two-player game that pitted players against each other in a battle between spaceships, demonstrating the potential of computers to create engaging and interactive experiences.
Early Experiments in Arcade Gaming:
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, the rise of arcade gaming marked a significant milestone in the evolution of interactive entertainment. Pioneering companies such as Atari, Nutting Associates, and Midway Games introduced a new generation of electromechanical and video-based arcade games that captured the imaginations of players around the world. Games like “Pong” (1972), “Space Invaders” (1978), and “Pac-Man” (1980) became cultural phenomena, paving the way for the emergence of home gaming consoles and personal computers.
The Advent of Home Gaming Consoles:
The 1970s saw the rise of home gaming consoles, bringing the excitement of arcade gaming into the living room. Companies like Magnavox, Atari, and Nintendo introduced a new generation of electronic devices that allowed players to enjoy video games in the comfort of their own homes. The Magnavox Odyssey, released in 1972, is widely considered the first home gaming console, featuring a collection of simple games that could be played on a television screen using plastic overlays and a set of controllers.
The Rise of Personal Computers:
The advent of personal computers in the 1970s and 1980s opened up new possibilities for gaming, providing developers with powerful tools and platforms to create more sophisticated and immersive experiences. Early home computers such as the Apple II, Commodore 64, and IBM PC became popular platforms for gaming, offering a wide range of software titles and game development tools. Games like “Adventure” (1976), “Zork” (1980), and “Ultima” (1981) demonstrated the potential of personal computers to deliver immersive storytelling and rich gameplay experiences.
Experimental Prototypes and Conceptual Innovations:
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, researchers and engineers continued to explore the possibilities of interactive entertainment, experimenting with new technologies and conceptual innovations that would shape the future of gaming. Early experiments in virtual reality, motion control, and augmented reality laid the groundwork for future advancements in gaming technology, while conceptual innovations such as networked multiplayer gaming and online communities foreshadowed the social and collaborative nature of modern gaming.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Pioneering Beginnings:
The pioneering beginnings of gaming laid the foundation for the digital revolution that would follow, shaping the industry into the vibrant and dynamic ecosystem it is today. From the early experiments and prototypes of the 1960s to the rise of home gaming consoles and personal computers in the 1970s and 1980s, these formative years paved the way for the evolution of gaming into a global phenomenon that transcends boundaries of age, gender, and culture. As we look back on the pioneering beginnings of gaming, we celebrate the visionaries and innovators who dared to dream of a world where interactive entertainment would captivate the hearts and minds of players around the world.
Commercialization Attempts: Rise and Fall in the 1990s:
The 1990s saw the first attempts to commercialize VR gaming with the release of products such as the Virtuality arcade machines and the Nintendo Virtual Boy. While these early systems showcased the potential of VR technology, they were hampered by limitations such as low-resolution graphics, cumbersome hardware, and high costs. As a result, consumer interest waned, and VR gaming fell out of favor for much of the decade.
Commercialization Attempts in Gaming: A Journey of Innovation and Adaptation:
The commercialization of gaming marks a pivotal moment in the history of interactive entertainment, where gaming evolved from experimental prototypes to a multi-billion dollar industry that captures the imaginations of millions of players worldwide. This article explores the various commercialization attempts in gaming, tracing the industry’s evolution from its humble beginnings to the global phenomenon it is today.
Arcade Era: The Birth of Coin-Op Gaming:
The commercialization of gaming can be traced back to the arcade era of the 1970s and 1980s, where the rise of coin-operated arcade machines introduced a new form of entertainment to the masses. Pioneering companies like Atari, Midway Games, and Namco created a wide range of electromechanical and video-based arcade games that captivated players with their simple yet addictive gameplay. Games like “Pong,” “Space Invaders,” and “Pac-Man” became cultural phenomena, drawing crowds of players to arcades around the world and laying the groundwork for the commercialization of gaming.
Home Gaming Consoles: Bringing Gaming into the Living Room:
The 1980s saw the emergence of home gaming consoles, bringing the excitement of arcade gaming into the living room. Companies like Nintendo, Sega, and Atari introduced a new generation of electronic devices that allowed players to enjoy video games in the comfort of their own homes. The release of consoles such as the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES), Sega Genesis, and Atari 2600 brought gaming to a wider audience, making it more accessible and affordable than ever before. With iconic titles like “Super Mario Bros.,” “Sonic the Hedgehog,” and “Pac-Man,” home gaming consoles became a staple of family entertainment and a driving force behind the commercialization of gaming.
PC Gaming: The Rise of Personal Computers:
The advent of personal computers in the 1980s and 1990s opened up new opportunities for gaming, providing developers with powerful platforms to create more sophisticated and immersive experiences. Early home computers like the Commodore 64, Apple II, and IBM PC became popular platforms for gaming, offering a wide range of software titles and game development tools. Games like “Doom,” “SimCity,” and “Civilization” demonstrated the potential of personal computers to deliver immersive storytelling and complex gameplay experiences, further fueling the commercialization of gaming.
Online Gaming: Connecting Players Around the World:
The 1990s saw the emergence of online gaming, where players could connect and compete with each other over the internet. The rise of online gaming services like America Online (AOL), CompuServe, and Blizzard Entertainment’s Battle.net provided players with a platform to play multiplayer games, chat with friends, and participate in online communities. Games like “Quake,” “StarCraft,” and “EverQuest” became early pioneers of online gaming, demonstrating the potential of the internet to connect players around the world and fuel the commercialization of gaming.
Mobile Gaming: Gaming on the Go:
In the 2000s, the rise of mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets opened up new opportunities for gaming, allowing players to enjoy games on the go. The launch of mobile platforms like Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android provided developers with a new distribution channel for games, leading to the rise of mobile gaming as a dominant force in the industry. Games like “Angry Birds,” “Candy Crush Saga,” and “Pokémon GO” became global sensations, demonstrating the potential of mobile gaming to reach a wide audience and generate significant revenue.
Conclusion: A Thriving Industry Built on Innovation:
The commercialization of gaming has transformed the industry into a thriving ecosystem of innovation, creativity, and entrepreneurship. From the arcade era of the 1970s to the rise of home gaming consoles, personal computers, online gaming, and mobile gaming, the evolution of gaming has been driven by a relentless pursuit of new technologies, platforms, and business models. As we look to the future, the commercialization of gaming continues to evolve, with emerging technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and cloud gaming promising to redefine the way we play, engage, and interact with games.
Revival and Reinvention: The Modern Era of VR Gaming:
The true revival of VR gaming began in the early 2010s with the emergence of new technologies and the rise of startups like Oculus VR. The 2012 Kickstarter campaign for the Oculus Rift, spearheaded by Palmer Luckey, reignited interest in VR gaming and generated widespread excitement among developers and gamers alike. The subsequent acquisition of Oculus VR by Facebook in 2014 further solidified VR’s place in the gaming industry and signaled the beginning of a new era for the technology.
Revival and Reinvention: The Modern Era of VR Gaming:
The modern era of virtual reality (VR) gaming represents a transformative period in the evolution of interactive entertainment. After decades of experimentation and false starts, VR technology has finally matured to a point where it offers immersive, engaging, and accessible gaming experiences that captivate players around the world. This article explores the revival and reinvention of VR gaming in the modern era, highlighting key milestones, technological advancements, and cultural shifts that have propelled the medium to new heights of popularity and innovation.
The Birth of Consumer-Grade VR Systems:
The modern era of VR gaming began in earnest with the launch of consumer-grade VR systems in the early 2010s. The 2012 Kickstarter campaign for the Oculus Rift, spearheaded by Palmer Luckey, ignited widespread excitement and anticipation for a new generation of VR technology. The subsequent acquisition of Oculus VR by Facebook in 2014 further solidified VR’s place in the gaming industry and signaled the beginning of a new era for the technology.
Technological Advancements and Innovations:
Since the launch of consumer-grade VR systems, the technology has undergone rapid advancements and innovations. High-resolution displays, precise motion tracking, and ergonomic designs have made modern VR headsets more comfortable, immersive, and user-friendly than ever before. In addition, advancements in graphics rendering, spatial audio, and haptic feedback have enhanced the realism and immersion of VR gaming experiences, allowing players to truly feel like they are part of the virtual world.
Diverse Content and Experiences:
One of the most significant developments in modern VR gaming is the proliferation of diverse content and experiences. From immersive narrative adventures and action-packed shooters to creative sandbox games and social experiences, VR offers something for every type of gamer. Developers have embraced the medium’s unique capabilities to create innovative and compelling experiences that push the boundaries of storytelling, gameplay, and interactivity, attracting players of all ages and interests.
Mainstream Adoption and Market Growth:
VR gaming has experienced steady growth and mainstream adoption in recent years, thanks in part to the success of popular VR titles such as Beat Saber, Superhot VR, and Half-Life: Alyx. In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of VR technology as people sought out new forms of entertainment and social interaction while staying at home. As a result, VR gaming has become more accessible and affordable, with an expanding library of titles and a growing community of players worldwide.
Future Directions and Potential:
Looking ahead, the future of VR gaming is bright, with continued advancements in technology and content creation driving innovation and growth in the industry. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), cloud gaming, and haptic feedback promise to further enhance the immersive capabilities of VR gaming and expand its reach to new audiences. With continued investment and development, VR gaming is poised to become an integral part of the gaming landscape, offering players immersive, interactive, and unforgettable experiences for years to come.
Consumer-Grade VR Systems: The Dawn of a New Era:
In 2016, consumer-grade VR systems such as the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR hit the market, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of VR gaming. These systems offered high-quality graphics, precise motion tracking, and immersive experiences that surpassed anything seen before in the world of gaming. With the release of hit titles like Beat Saber, Superhot VR, and Half-Life: Alyx, VR gaming began to gain mainstream recognition and acceptance, attracting a growing community of players and developers.
Consumer-Grade VR Systems in Gaming: A New Frontier of Immersive Entertainment:
Consumer-grade virtual reality (VR) systems have ushered in a new era of immersive gaming experiences, allowing players to step into virtual worlds and interact with digital environments like never before. From the Oculus Rift to the HTC Vive and PlayStation VR, these cutting-edge devices have captivated gamers worldwide, offering a level of immersion and interactivity that was once only possible in science fiction. This article explores the evolution, impact, and future of consumer-grade VR systems in gaming.
The Birth of Consumer-Grade VR Systems:
The concept of consumer-grade VR systems first gained widespread attention with the launch of the Oculus Rift Kickstarter campaign in 2012. Palmer Luckey, the founder of Oculus VR, set out to create an affordable VR headset that could deliver immersive gaming experiences to consumers. The campaign was a resounding success, raising over $2 million and generating widespread excitement and anticipation for the future of VR gaming.
Key Players in the Market:
Since the launch of the Oculus Rift, several other companies have entered the consumer-grade VR market, each with their own unique offerings and approaches to VR gaming. HTC Vive, developed in collaboration with Valve Corporation, introduced room-scale tracking and motion controllers, allowing players to move freely and interact with their virtual environment. PlayStation VR, developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, leverages the power of the PlayStation 4 console to deliver high-quality VR experiences to console gamers.
Technological Advancements:
One of the key factors driving the success of consumer-grade VR systems is the rapid advancement of VR technology. High-resolution displays, precise motion tracking, and ergonomic designs have made modern VR headsets more comfortable, immersive, and user-friendly than ever before. Inside-out tracking systems eliminate the need for external sensors, while advancements in optics and display technology reduce motion sickness and improve visual fidelity.
Diverse Content and Experiences:
Consumer-grade VR systems offer a diverse range of content and experiences, catering to a wide variety of gaming preferences and interests. From immersive narrative adventures and action-packed shooters to creative sandbox games and social experiences, VR gaming has something for everyone. Developers have embraced the medium’s unique capabilities to create innovative and compelling experiences that push the boundaries of storytelling, gameplay, and interactivity.
Mainstream Adoption and Market Growth:
VR gaming has experienced steady growth and mainstream adoption in recent years, thanks in part to the success of popular VR titles and the continued investment in VR technology. The COVID-19 pandemic also accelerated the adoption of VR technology as people sought out new forms of entertainment and social interaction while staying at home. As a result, VR gaming has become more accessible and affordable, with an expanding library of titles and a growing community of players worldwide.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite its many successes, consumer-grade VR still faces challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption. These include concerns about affordability, comfort, and content availability, as well as technical limitations such as motion sickness and latency. However, as technology continues to evolve and improve, the future of consumer-grade VR systems in gaming looks promising. With continued investment in hardware, software, and content creation, VR gaming has the potential to revolutionize the gaming industry and redefine the way we play, engage, and interact with games.
Technological Advancements: Pushing the Boundaries of Possibility:
Since the launch of consumer-grade VR systems, the technology has continued to evolve and improve at a rapid pace. Advances in display technology, graphics rendering, and motion tracking have made VR experiences more immersive and realistic than ever before. In addition, the development of accessories such as hand-tracking controllers, haptic feedback devices, and omnidirectional treadmills has enhanced the level of interactivity and immersion in VR gaming, further blurring the lines between the virtual and the real.
Technological Advancements: Pushing the Boundaries of Possibility in Gaming:
Technological advancements have always been at the forefront of pushing the boundaries of possibility in gaming. From the early days of pixelated sprites to the cutting-edge graphics and immersive experiences of today, gaming technology has evolved at a rapid pace, driving innovation and shaping the way we play, create, and experience games. This article explores the transformative impact of technological advancements on gaming, highlighting key developments and innovations that have revolutionized the industry.
Graphics Rendering and Visual Fidelity:
One of the most noticeable advancements in gaming technology is in graphics rendering and visual fidelity. Over the years, we’ve witnessed a dramatic improvement in the quality of graphics, from simple 2D sprites to photorealistic 3D environments. This evolution has been driven by advancements in hardware capabilities, including faster processors, more powerful graphics cards, and higher-resolution displays. Today’s games feature stunningly detailed textures, realistic lighting effects, and lifelike character animations, creating immersive worlds that rival those found in movies and television.
Physics Simulation and Realism:
Another area where technological advancements have pushed the boundaries of possibility in gaming is in physics simulation and realism. Early games relied on simple physics models and rigid body dynamics, but today’s games feature sophisticated physics engines that accurately simulate the behavior of objects, particles, and materials in real-time. This allows for more realistic interactions between players and their environments, as well as more dynamic and immersive gameplay experiences.
Artificial Intelligence and Behavioral Modeling:
Artificial intelligence (AI) has also played a crucial role in advancing gaming technology, particularly in the realm of non-player character (NPC) behavior and enemy intelligence. Early NPCs were often limited to simple patterns and scripted actions, but modern AI systems use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to create more lifelike and responsive characters. This allows NPCs to adapt to changing situations, learn from their experiences, and exhibit more nuanced behaviors, enhancing the overall immersion and realism of the gaming experience.
Networking and Multiplayer Connectivity:
The advent of networking technology has transformed gaming from a solitary activity into a social phenomenon. Online multiplayer gaming has become increasingly popular, allowing players to connect and compete with each other in real-time from anywhere in the world. Technological advancements in networking infrastructure, including high-speed internet connections and dedicated servers, have made online gaming more accessible and reliable than ever before, leading to the rise of esports and competitive gaming as major industry sectors.
Virtual Reality and Immersive Experiences:
Perhaps the most revolutionary advancement in gaming technology in recent years has been the rise of virtual reality (VR) and immersive experiences. VR technology allows players to step into virtual worlds and interact with their environments using specialized headsets and motion-tracking controllers. This level of immersion offers a truly transformative gaming experience, allowing players to explore new worlds, solve puzzles, and engage in epic battles like never before. With continued advancements in VR hardware and software, the possibilities for immersive gaming experiences are virtually limitless.
Conclusion: The Future of Gaming Technology:
As technology continues to evolve and improve, the future of gaming technology looks brighter than ever. From advancements in graphics rendering and physics simulation to the rise of artificial intelligence and virtual reality, the possibilities for pushing the boundaries of possibility in gaming are endless. Whether it’s creating more immersive experiences, enhancing social connectivity, or pushing the limits of storytelling and gameplay, technological advancements will continue to drive innovation and shape the future of gaming for years to come.
Diverse Content and Experiences: From Games to Virtual Worlds:
One of the most exciting aspects of VR gaming is the diverse range of content and experiences it offers. From immersive narrative adventures and action-packed shooters to creative sandbox games and social experiences, VR gaming caters to a wide variety of tastes and preferences. Developers have embraced the medium’s unique capabilities to create innovative and compelling experiences that push the boundaries of storytelling, gameplay, and interactivity, attracting players of all ages and interests.
Future Directions and Potential: Looking Ahead:
As we look to the future, the potential of VR gaming seems limitless. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), cloud gaming, and haptic feedback promise to further enhance the immersive capabilities of VR gaming and expand its reach to new audiences. With continued advancements in hardware, software, and content creation tools, VR gaming is poised to become an integral part of the gaming landscape, offering players immersive, interactive, and unforgettable experiences for years to come.











